Special Issue: Testing the Quality of GeoAI-Generated Data for VGI Mapping
🔗 View Special Issue
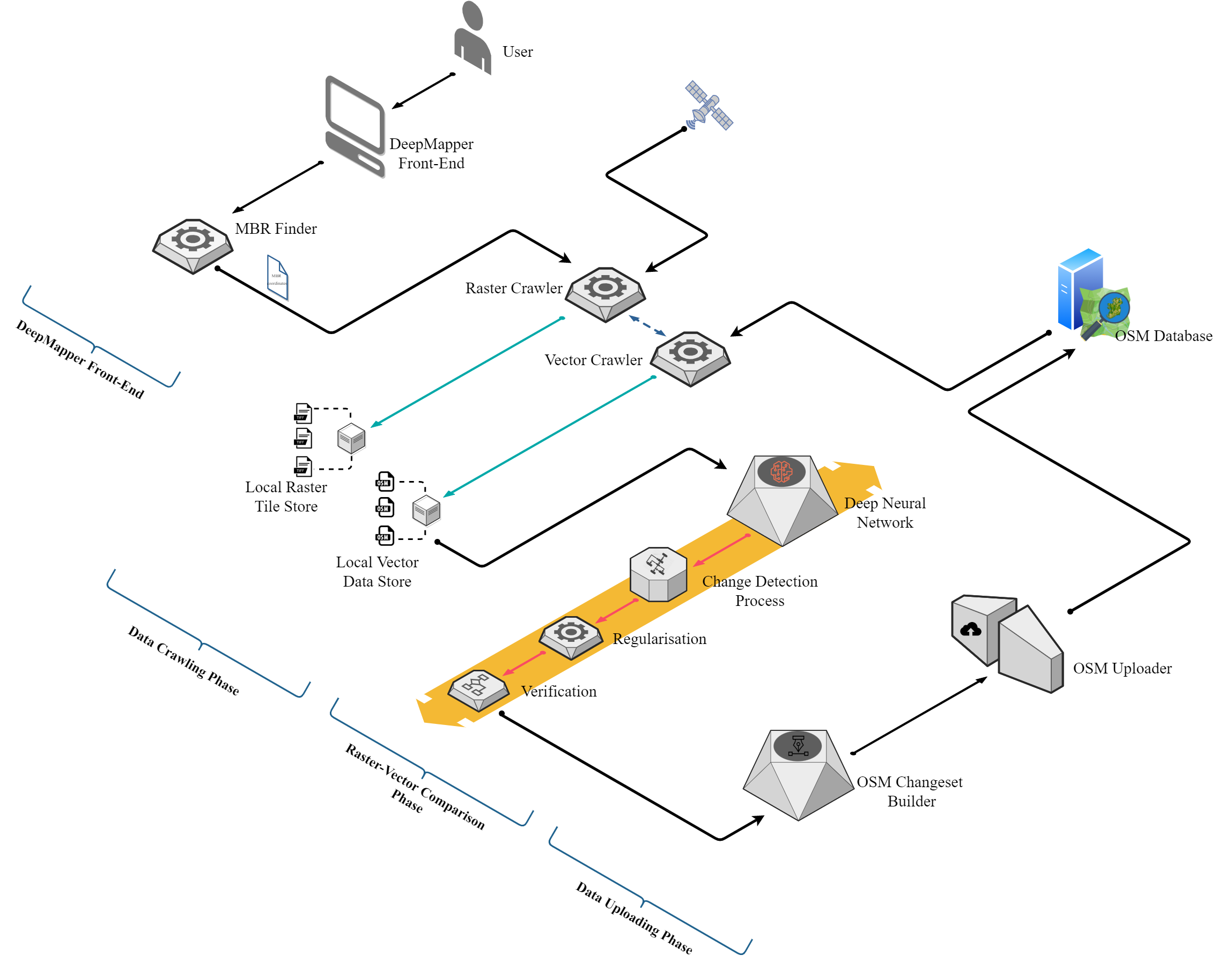
I am collaborating with Dr. James D. Carswell as a co-editor of this special issue, . Together, we are leading a timely and critical exploration into the reliability and accuracy of GeoAI-generated geospatial data, particularly within the context of Volunteered Geographic Information (VGI) platforms such as OpenStreetMap.
While GeoAI offers immense potential to automate and accelerate map production, the growing concern around data quality — often referred to as ‘AI slop’ (a term describing low-quality or error-prone outputs from artificial intelligence systems) — has raised important questions about the trustworthiness of AI-generated content. This special issue invites empirical research, case studies, and benchmark studies that evaluate how well current GeoAI models perform in real-world conditions, especially when compared to authoritative data sources and community-generated maps.
The issue focuses on:
🔎 Assessing accuracy and reliability of AI-predicted map features
🔎 Evaluating integration of GeoAI outputs into VGI platforms
🔎 Developing QA and benchmarking frameworks for AI-generated spatial data
🔎 Addressing challenges and future directions for AI-assisted mapping
Through this special issue, our goal is to inform both academic and practitioner communities about the current capabilities and limitations of GeoAI in collaborative mapping, and to foster a dialogue between automated approaches and human-led mapping practices.